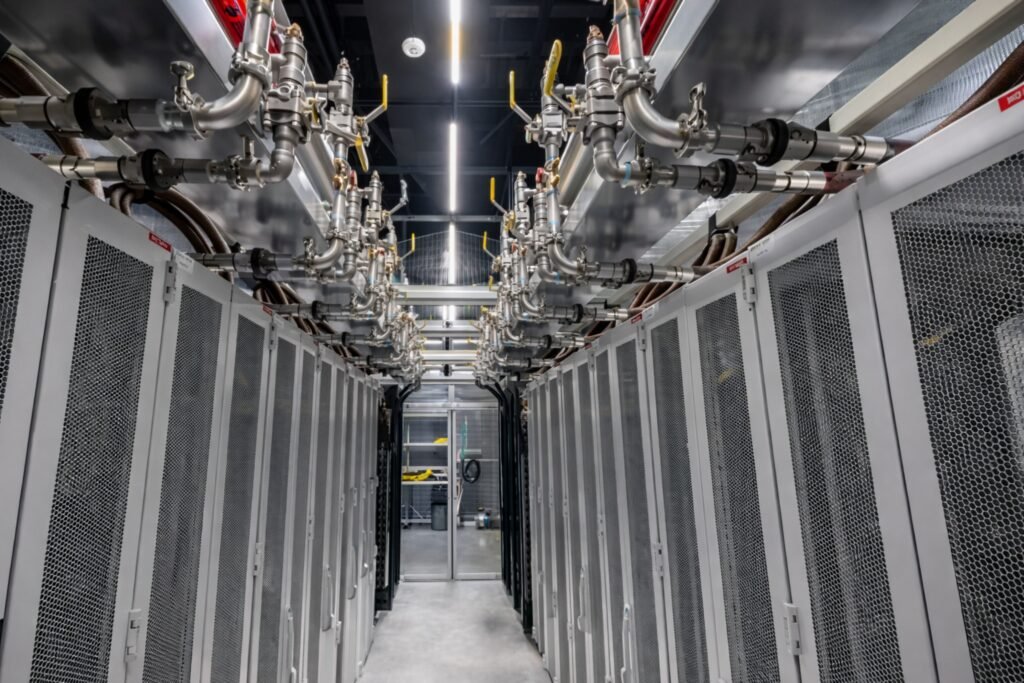
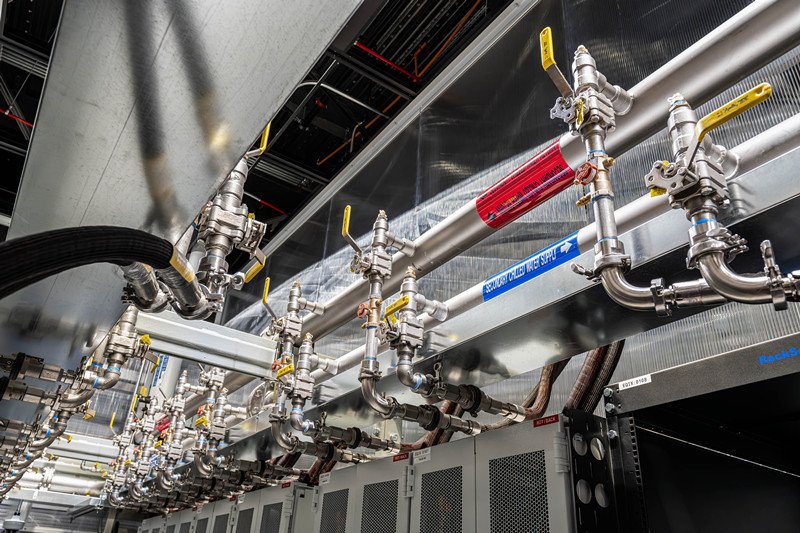
Data centers face rising heat, rising energy bills, and rising failure risks, but many teams still rely on outdated cooling designs that cannot scale with modern workloads.
Liquid cooling is now the most reliable way to support high-density computing in 2026 because it delivers higher thermal efficiency, lower energy costs, and better long-term reliability than air-based systems.
I want to walk you through how liquid cooling really works, where it delivers value, and how to design systems that scale without hidden risks.
Why Data Center Cooling Matters More Than Ever?
Overheating risks grow fast, energy costs keep rising, and downtime becomes more expensive every year, so cooling is no longer just a facilities problem.
Cooling now directly affects uptime, energy efficiency, and the total cost of running modern data centers.

The Rise of High-Density AI Workloads
AI and high-performance computing changed everything. A single rack today can exceed 40–100 kW, while traditional air cooling was designed for 5–10 kW. Air simply cannot remove heat fast enough at these densities.
Liquid cooling removes heat directly at the source. This prevents hotspots, stabilizes temperatures, and allows predictable scaling.
Cooling as a Driver of Energy Efficiency (PUE & OPEX)
Cooling power directly affects Power Usage Effectiveness. Liquid cooling reduces fan demand and allows higher supply temperatures, which lowers chiller energy use and total OPEX.
Risks of Suboptimal Thermal Management
Poor thermal design accelerates component aging, increases failure rates, and raises the risk of unplanned shutdowns. Most outages I have seen were caused by cooling instability, not power loss.
Comparing Cooling Technologies?
Choosing the right cooling approach determines long-term flexibility and cost.
Each cooling technology solves a different problem, and no single option fits every data center.

Air vs. Liquid Cooling – Pros and Cons
Air cooling is simple and familiar but inefficient at high density. Liquid cooling delivers superior heat transfer but requires higher design discipline and component quality.
Direct-to-Chip (D2C) vs. Immersion Cooling
D2C integrates well with existing racks and simplifies maintenance. Immersion cooling offers extreme heat removal but complicates operations and hardware compatibility.
Hybrid & Modular Cooling Architectures
Hybrid designs allow phased upgrades and reduce risk. Modular systems support future expansion without full redesign.
Key Components of a Liquid Cooling System?
A cooling loop is only as reliable as its weakest component.
Stainless steel components provide durability, cleanliness, and pressure stability for modern liquid cooling systems.
Liquid Cooling Fittings
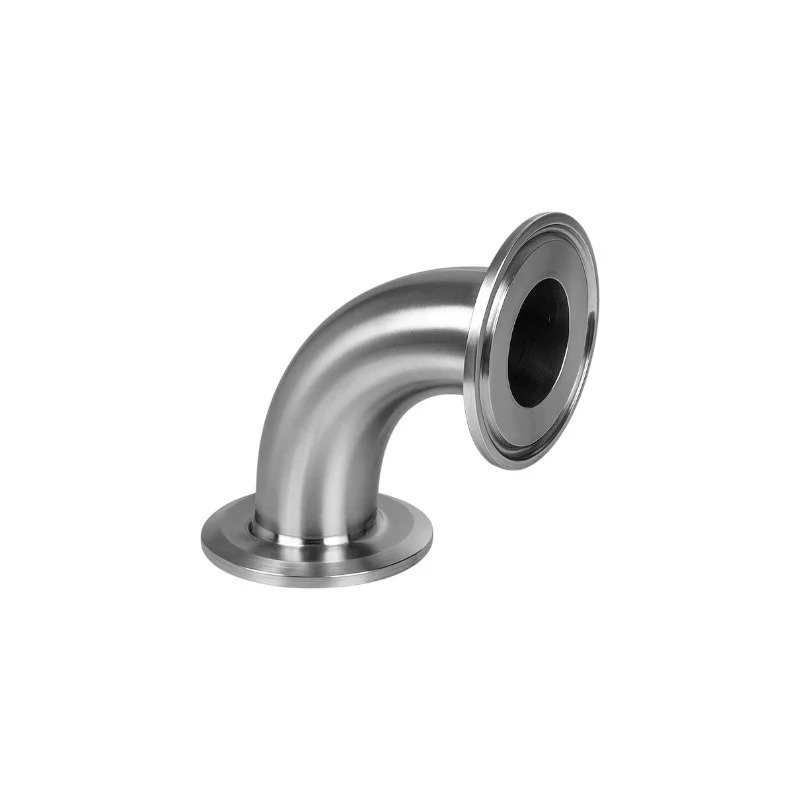

High-quality sanitary tri-clamp fittings reduce turbulence, pressure loss, and leak risk. ensure efficient, secure, and reliable fluid transfer in any cooling process.
Stainless Steel Tubing

304 and 316 stainless steel tubing offers corrosion resistance, dimensional stability, and predictable pressure performance across temperature cycles, which is ideal for seamless integration in cooling systems.
Sanitary Valves
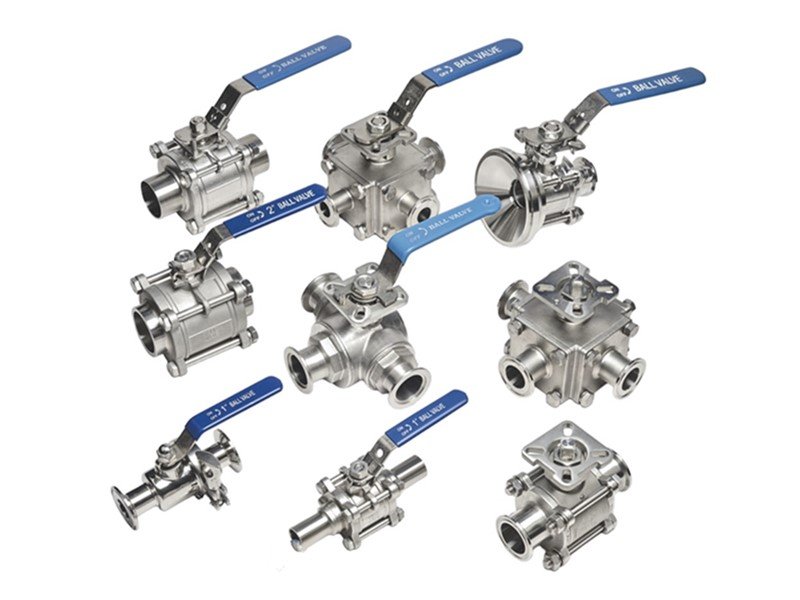

Precision-engineered sanitary valves ensure reliable flow control and optimized performance for data center cooling systems.
Adapters

Versatile NPT/BSP adapters to connect and customize your liquid cooling system components. Typically sourced in 304 and 316L stainless steel.
Why Stainless Steel? A Material Science Breakdown?
Material selection determines system lifespan and reliability.
Stainless steel delivers the best balance of safety, durability, and total cost of ownership.

304 vs. 316 Stainless: Corrosion Resistance & Cost
316 stainless offers superior resistance to chlorides and aggressive coolants due to added molybdenum.
| Material | Corrosion Resistance | Cost | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 SS | Good | Lower | Standard loops |
| 316 SS | Excellent | Medium | Critical systems |
| Copper | Moderate | High | Legacy systems |
| Polymer | Low–Moderate | Low | Short-term use |
Metal vs. Plastic Tubing
Plastic tubing degrades, expands, and absorbs additives. Stainless steel remains stable under pressure and temperature variation.
Total Cost of Ownership
Stainless steel systems cost more upfront but reduce downtime, maintenance, and replacement costs over time.
Designing Your Cooling Architecture?
Design discipline defines success.
Good architecture balances redundancy, control, and simplicity.

Redundant Loop Design & Failover Planning
Dual pumps, isolation valves, and parallel loops allow maintenance without shutdown.
Flow Rate, Pressure, and Thermal Transfer Calculations
Component geometry affects pressure drop and heat transfer. Poor design increases pumping energy and reduces efficiency.
Leak Detection and Monitoring
Sensors, automated valves, and zoning minimize risk and limit damage when failures occur.
Performance & Energy Metrics?
Measurement enables optimization.
Liquid cooling delivers value only when performance is monitored and controlled.
Impact on PUE
Liquid cooling reduces fan power and stabilizes temperatures, often improving PUE from 1.6 to below 1.3.
Case Example: 20% Energy Reduction
A high-density upgrade using D2C cooling reduced cooling energy by 20% with a payback period under three years.
Predictive Monitoring
Smart valves and flow sensors optimize performance during workload spikes.
Implementation Roadmap?
Execution determines ROI.
A phased rollout minimizes risk and protects capital.
Retrofitting Existing Data Centers
Start with high-density racks and use hybrid designs to reduce disruption.
Sourcing and RFQ Tips
Verify material certificates, pressure ratings, and surface finish. Standardize components early.
Maintenance Planning
Define inspection, flushing, and spare strategies. Stainless steel simplifies long-term maintenance.
Real-World Case Studies?
Field results validate design choices.
Quality materials and good architecture reduce energy use, downtime, and maintenance.

Case 1 – AI Data Center Upgrade
Rack density increased from 15 kW to 60 kW with stable thermal performance.
Case 2 – Preventing Corrosion Failures
Replacing polymer loops with stainless steel eliminated leaks and reduced maintenance labor.
Before/After Results
Lower energy use, reduced downtime, and predictable maintenance.
FAQ – Common Liquid Cooling Questions?
What’s the difference between 304 and 316 stainless steel?
316 offers better corrosion resistance due to added molybdenum.
How do I choose between immersion and D2C cooling?
Choose D2C for easier maintenance. Choose immersion for extreme density with operational readiness.
Is stainless steel more expensive long-term?
No. Stainless steel delivers lower lifetime cost due to durability and reliability.
Conclusion – Build for Scalability, Reliability, and Efficiency?
Liquid cooling, combined with high-quality stainless steel components, enables scalable, reliable, and energy-efficient data centers built for future workloads.
Beyond Fluid is a leading supplier of stainless steel fittings and valves for the data center liquid cooling industry, delivering leak-free performance and long-lasting durability. Contact Us for more details.







