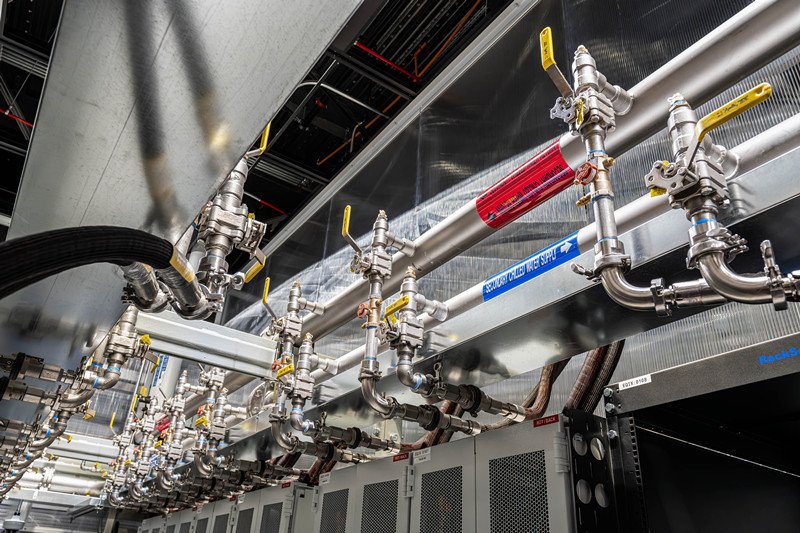
Downtime kills data centers, but cooling failures cause it.
Wrong fittings create leaks, corrosion, and pressure loss, so reliability collapses fast.
Stainless steel fittings are the safest and most reliable choice for data center cooling systems because they handle pressure, temperature, and water chemistry without leaks, corrosion, or premature failure.
I have worked with global OEMs for over 15 years, and I see the same pattern. Cooling failures rarely start with pumps or chillers. They start with poor material choices at the fitting level.
Data centers are not normal buildings. Their cooling infrastructure1 behaves more like an industrial process plant. That reality changes everything.
Why Data Centers Require Specialized Fittings?
High uptime targets and dense thermal loads push cooling systems to their limits.
Standard plumbing fittings fail silently until they cause shutdowns.
Data centers require specialized fittings because cooling systems operate continuously under high pressure, variable temperatures, strict water quality limits, and extreme uptime requirements.
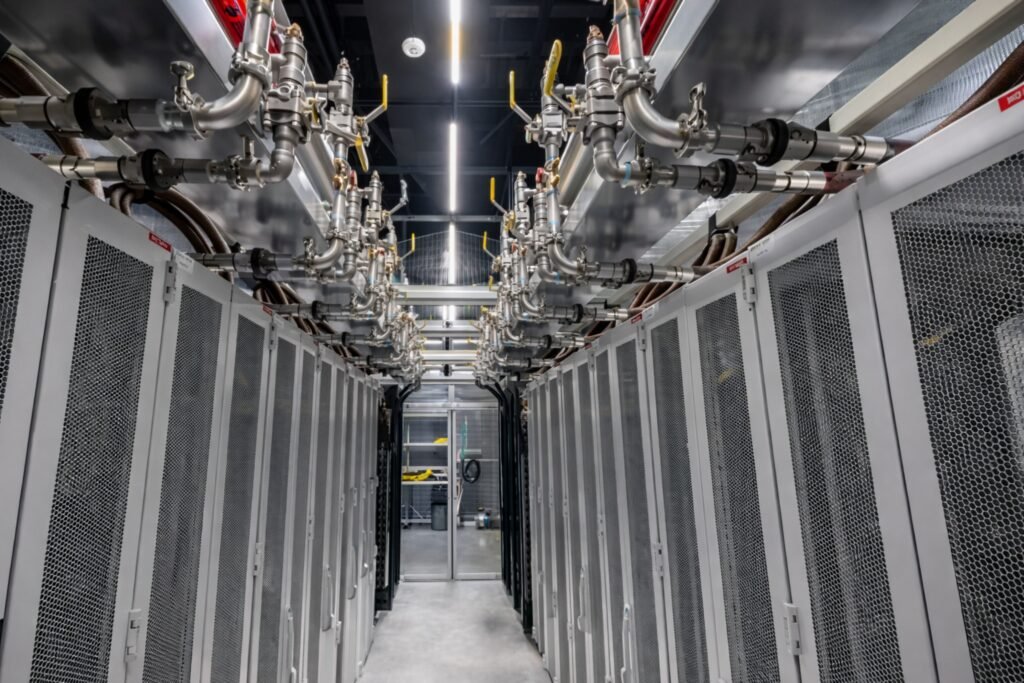

High uptime and zero-failure tolerance
A data center does not tolerate “minor” leaks.
A few drops per hour can damage servers, power distribution units, and containment systems.
In industrial plants, a leak means maintenance.
In data centers, a leak means outages, SLA penalties, and reputation damage.
This changes how I think about fittings.
The goal is not just to meet pressure ratings. The goal is to eliminate leak paths over decades of operation.
Thread quality, surface finish, and material stability matter more than initial cost.
Thermal load and pressure demands
Modern data centers generate extreme heat density.
Chilled water systems operate with constant flow, pressure fluctuations, and thermal cycling.
Direct-to-chip and rear door systems push pressures even higher.
Fittings see expansion, contraction, and vibration every day.
Materials that creep, soften, or fatigue will fail.
Stainless steel maintains strength across wide temperature ranges, which is critical in these environments.
Water quality and corrosion risks
Closed-loop cooling water is never “pure.”
It contains oxygen, glycol, biocides, and corrosion inhibitors.
Lower-grade metals react with these additives.
Once corrosion starts, it accelerates fast.
I have seen systems where fittings looked fine externally but were pitted inside.
Stainless steel resists this internal attack far better than carbon steel or copper alloys.
Space, scalability, and maintenance constraints
Data centers are dense.
There is limited space for tools, repairs, and replacements.
Fittings must install cleanly and stay sealed for years.
Frequent rework is not acceptable.
This is why compact, high-integrity stainless steel fittings dominate modern designs.
Why Stainless Steel Is Ideal for Data Center Applications?
Cooling infrastructure demands stability, not shortcuts.
Material choice determines long-term reliability more than any other factor.
Stainless steel is ideal for data center fittings because it resists corrosion, maintains strength under pressure and heat, stays clean in closed-loop systems, and delivers lower lifecycle cost.

Corrosion Resistance in Closed-Loop Cooling Systems
Stainless steel forms a passive oxide layer that protects the base metal.
This layer regenerates automatically when exposed to oxygen.
In closed-loop systems, this behavior is critical.
Even low oxygen levels are enough to maintain protection.
Glycol mixtures, biocides, and pH adjustments attack weaker materials.
Stainless steel remains stable, so internal surfaces stay smooth.
Smooth surfaces reduce biofilm buildup and pressure loss over time.
Strength Under High Pressure and Temperature
Stainless steel maintains mechanical strength at elevated temperatures.
It does not soften like plastics or creep like some copper alloys.
This matters in high-pressure chilled water and liquid cooling loops.
Pressure spikes happen during pump startup, valve closure, and system balancing.
A fitting that deforms once never seals the same again.
Stainless steel resists this permanent deformation.
Hygiene, Cleanability, and Long-Term Stability
Clean systems cool better.
Any internal fouling reduces heat transfer efficiency.
Stainless steel has low surface roughness when properly manufactured.
It does not shed particles or react with water additives.
This stability makes flushing and commissioning more effective.
It also simplifies long-term maintenance planning.
Lifecycle Cost vs Initial Cost
Stainless steel fittings cost more upfront.
This is obvious and unavoidable.
But replacement costs in data centers are extreme.
Downtime, labor, and risk multiply the real expense.
Over 15 to 20 years, stainless steel is cheaper.
I advise buyers to compare lifecycle cost, not unit price.
Common Data Center Applications for Stainless Steel Fittings?
Cooling architectures are evolving fast.
Stainless steel adapts to all of them.
Stainless steel fittings are widely used in chilled water loops, direct-to-chip liquid cooling, rear door heat exchangers, and immersion cooling infrastructure.
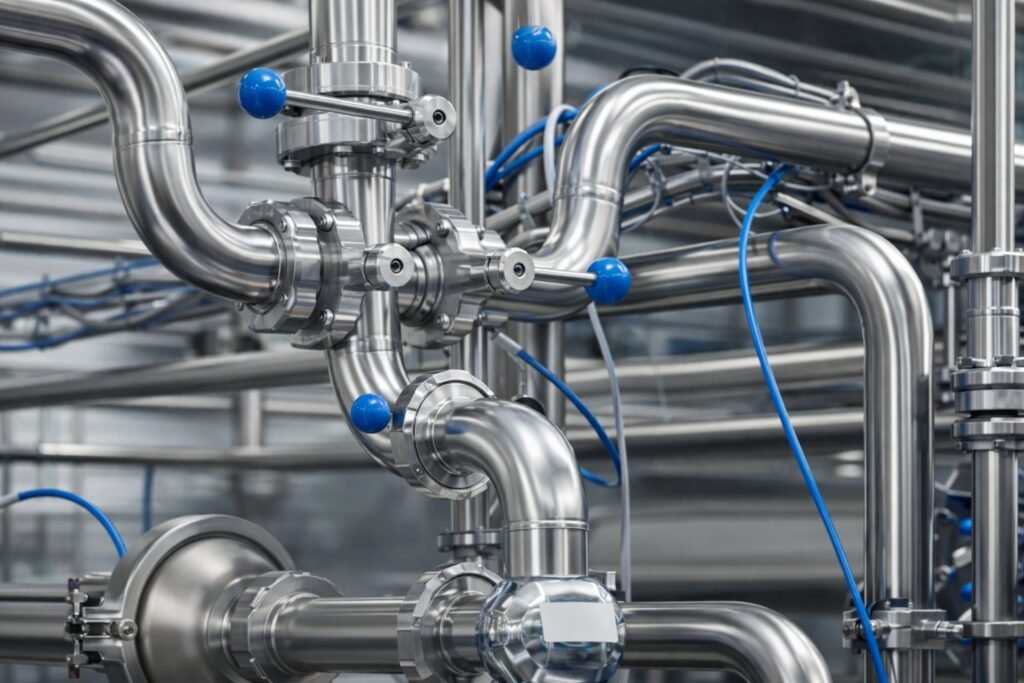

Chilled Water Cooling Loops
This is still the backbone of most data centers.
Large diameter pipes, constant flow, and long service life define these systems.
Stainless steel fittings handle vibration and thermal cycling better than carbon steel.
They also reduce internal corrosion products that clog strainers and valves.
Direct-to-Chip Liquid Cooling
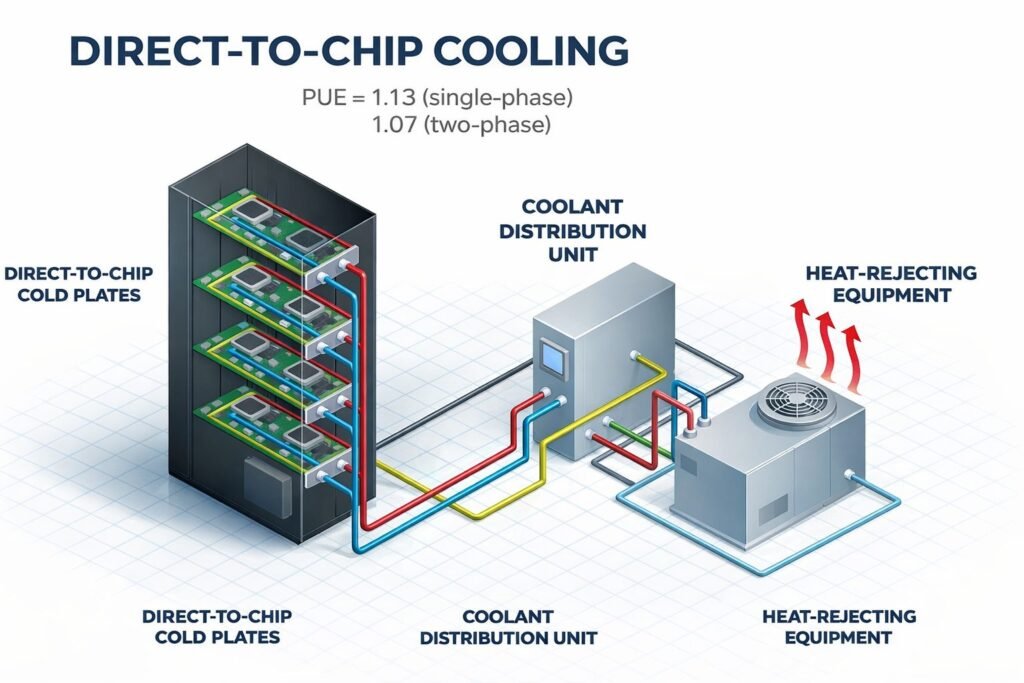
Direct-to-chip systems2 operate closer to IT hardware.
Leak risk is the primary concern.
Here, fitting integrity is non-negotiable.
Stainless steel provides consistent torque retention and sealing stability.
This reduces micro-leaks that would otherwise go unnoticed until failure.
Rear Door Heat Exchangers

Rear door systems3 add weight and movement to racks.
This introduces mechanical stress into piping connections.
Stainless steel fittings tolerate this stress better than softer materials.
They maintain alignment and sealing even under minor movement.
Immersion Cooling Infrastructure
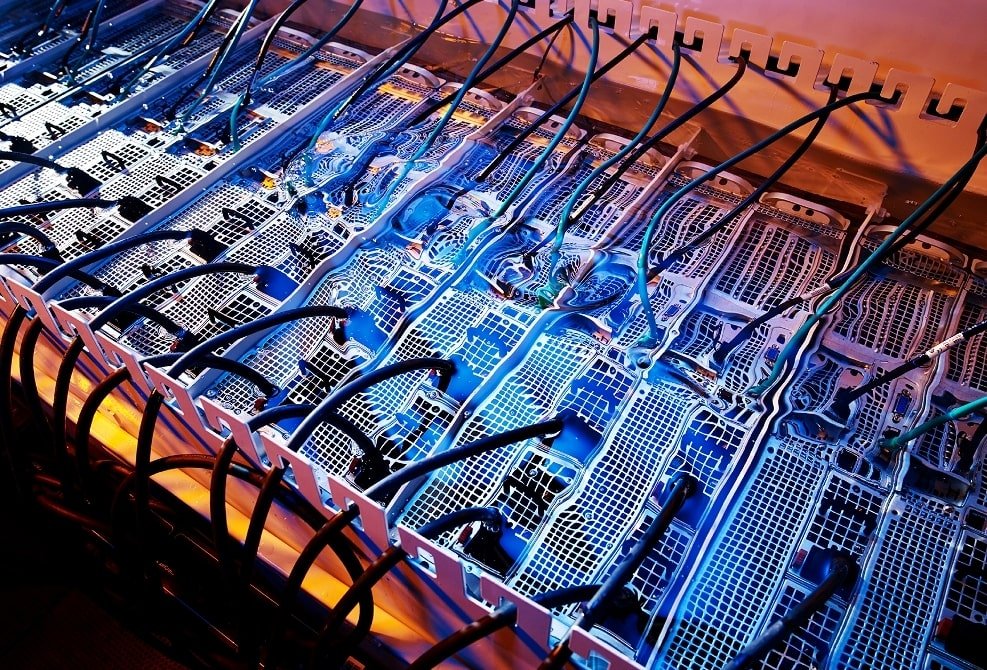
Immersion cooling4 uses specialized fluids and higher temperatures.
Material compatibility becomes critical.
Stainless steel resists chemical interaction with most dielectric fluids.
It also supports modular expansion without degrading performance.
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Fittings?
Not all stainless steel fittings are equal.
Material grade and connection type matter.
Choosing the right stainless steel fittings requires matching grade, connection method, pressure rating, and coolant compatibility to the specific cooling design.
304 vs 316 Stainless Steel – Which to Use and Why

304 stainless steel works in clean, low-chloride systems.
It is common in basic chilled water loops.
316 stainless steel adds molybdenum.
This improves resistance to chlorides and aggressive additives.
I recommend 316 for most data centers.
The cost difference is small compared to risk reduction.
Threaded vs Welded vs Clamp Connections

Threaded fittings install fast but introduce leak paths.
They rely on correct torque and sealing practices.
Welded connections eliminate leak paths but reduce flexibility.
They require skilled installation and planning.
Clamp and compression fittings balance both needs.
They allow modular expansion with high sealing integrity.
Pressure Ratings and Temperature Limits
Always check working pressure, not burst pressure.
Cooling systems operate continuously.
Temperature reduces pressure ratings over time.
Ignoring this shortens fitting life.
I advise building in safety margins from the start.
Compatibility with Coolants and Additives
Glycol concentration, pH, and inhibitors affect materials.
Always confirm compatibility.
Stainless steel handles most formulations well.
Plastics and mixed metals often do not.
Stainless Steel vs Other Materials in Data Centers?
Material trade-offs define system risk.
Shortcuts show up years later.
Stainless steel outperforms copper, carbon steel, and plastic fittings in reliability, corrosion resistance, and long-term stability for data center cooling systems.
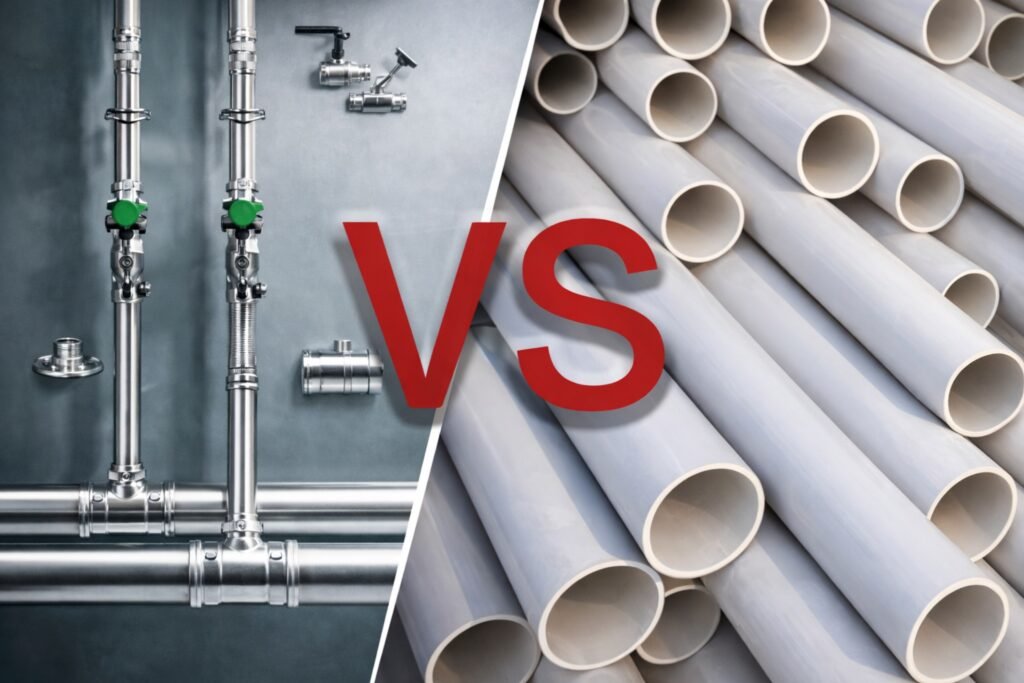

Stainless Steel vs Copper
Copper transfers heat well but corrodes in treated water.
It also work-hardens under vibration.
Leaks often appear at joints after years of operation.
Stainless steel avoids this fatigue.
Stainless Steel vs Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is cheap but corrodes internally.
Corrosion products clog valves and reduce flow.
Protective coatings fail over time.
Stainless steel does not rely on coatings.
Stainless Steel vs Plastic / Composite Fittings
Plastics are easy to install but creep under pressure.
They also age poorly under heat.
In critical environments, I avoid plastic fittings entirely.
Standards, Compliance, and Risk Reduction?
Compliance protects both engineers and buyers.
It also simplifies internal approvals.
Using stainless steel fittings manufactured to recognized standards reduces leak risk, simplifies compliance, and supports long-term operational safety.

ASME, ASTM, and ISO Standards
Standards define material chemistry and mechanical properties.
They reduce uncertainty.
Certified stainless steel fittings provide traceability.
This matters during audits and incident investigations.
Preventing Leaks and Corrosion Failures
Good material is not enough.
Installation practices matter.
Clean cutting, correct torque, and system flushing prevent early failures.
I always stress training during commissioning.
Best Practices for Installation and Maintenance
Plan access for inspection.
Avoid mixing dissimilar metals.
Document materials and certificates from day one.
This simplifies future upgrades.
Frequently Asked Questions (Engineer-Focused)?
Engineers ask practical questions.
These answers reflect real projects.
Stainless steel fittings typically last decades, work with glycol-based coolants, fail mainly due to installation errors, and support high cooling efficiency through stable flow and clean internal surfaces.
How long do stainless steel fittings last in data centers?
With proper installation, over 20 years is common.
Many systems run much longer.
Are stainless steel fittings compatible with glycol-based coolants?
Yes, especially 316 stainless steel.
Compatibility is excellent with standard formulations.
What are the most common failure modes?
Improper installation causes most failures.
Material defects are rare when standards are followed.
How do fittings affect overall cooling efficiency?
Smooth, corrosion-free fittings maintain flow rates.
Stable flow improves heat removal efficiency.
Conclusion
Stainless steel fittings protect data center cooling systems from leaks, corrosion, and downtime, making them the safest long-term choice for high-density, high-reliability infrastructure.
Partner with Beyond Fluid
Beyond Fluid a leading supplier of stainless steel fittings for data center cooling systems. Contact Us for more details.
-
Understanding cooling infrastructure is crucial for optimizing data center efficiency and performance. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how Direct-to-chip systems enhance performance and efficiency in IT hardware. ↩
-
Explore how Rear door systems enhance rack functionality and efficiency. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the principles and benefits of immersion cooling technology. ↩







