Efficient and safe fluid control is vital for any industrial system. Manifold valves play a critical role in achieving this, ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance in various applications.
Manifold valves are essential components of industrial systems, providing precise control, isolation, and balancing for hydraulic and pneumatic processes. Their versatility makes them indispensable across multiple industries.
Understanding the functionality, types, and best practices for manifold valves can help you make informed decisions, ensuring reliability and efficiency in your operations.
What Are Manifold Valves and Why Are They Important?

Manifold valves serve as multi-functional devices designed to manage fluid control in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. They perform critical tasks like isolation, venting, and balancing to streamline operations and maintain safety.
Manifold valves are compact, combining several valve functions into a single block. They simplify fluid control, reduce leakage risks, and improve system efficiency.
Beyond their practicality, manifold valves contribute significantly to minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth maintenance in demanding environments.
What Are the Types of Manifold Valves?
Two-Valve Manifold: Features and Use Cases
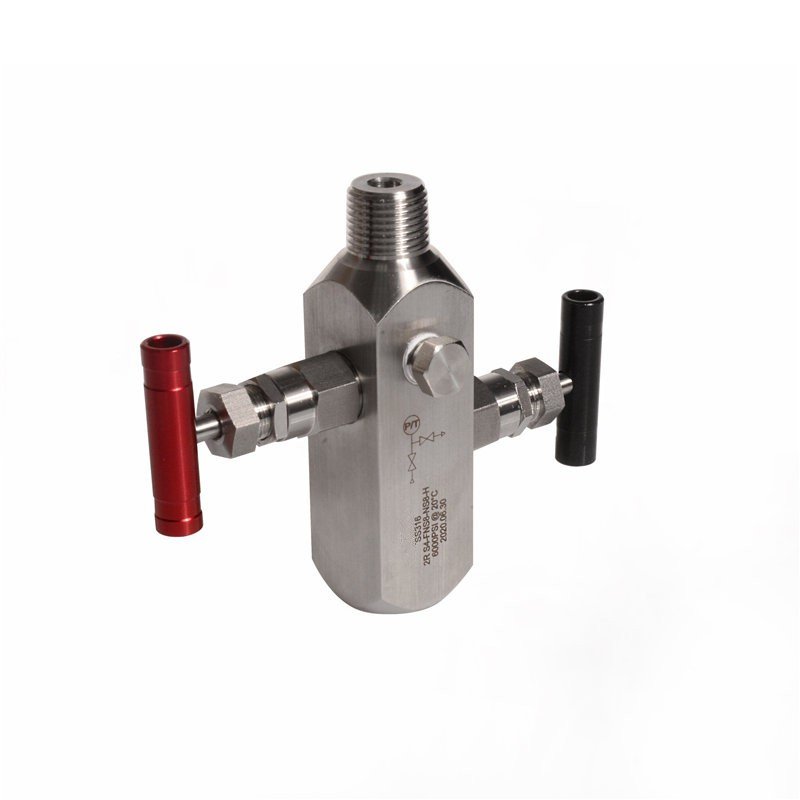

Two-valve manifolds consist of one isolation valve and one vent valve. This straightforward design makes them ideal for simpler applications.
Two-valve manifolds are commonly used to isolate and vent pressure gauges for calibration or maintenance purposes.
How Two-Valve Manifolds Work
Two-valve manifolds operate by isolating the pressure gauge from the system pressure using the isolation valve. The vent valve allows for controlled pressure release, enabling safe calibration or replacement. These manifolds are valued for their simplicity, compact size, and cost-effectiveness in low-complexity systems.
Three-Valve Manifold: Features and Use Cases
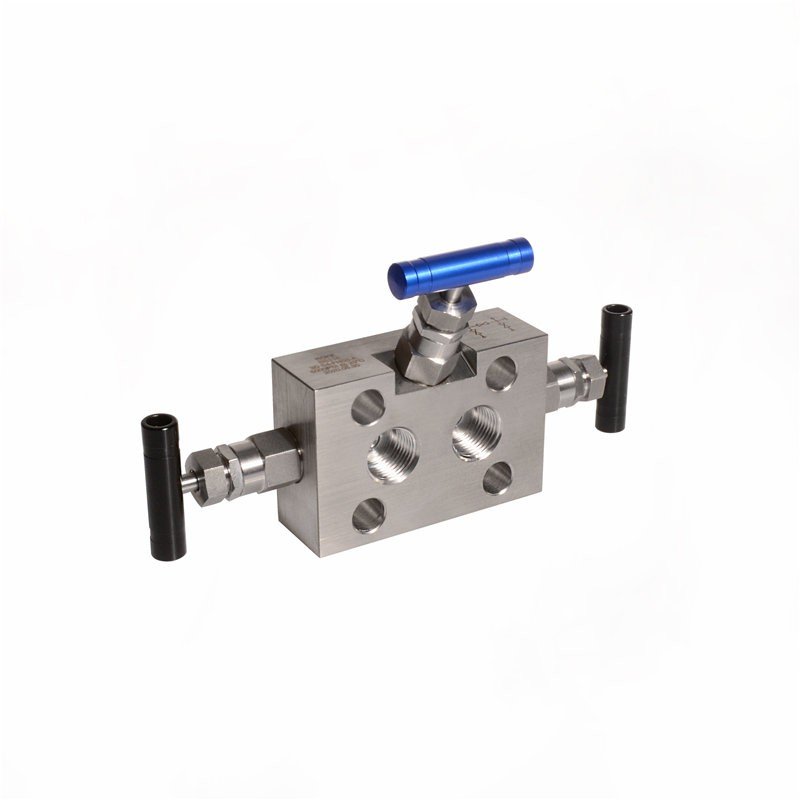

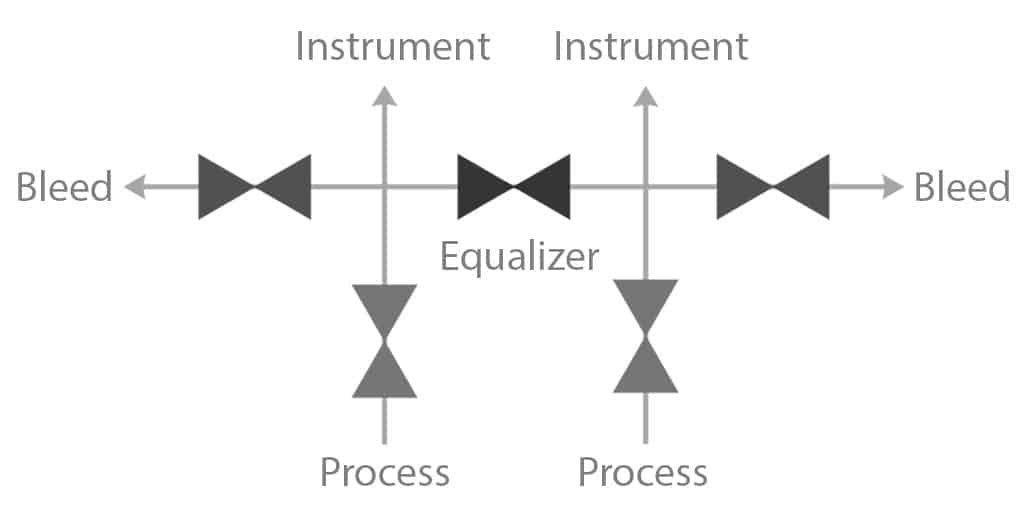
Three-valve manifolds include two isolation valves and one equalizing valve. This configuration provides more functionality for differential pressure measurement.
Three-valve manifolds are indispensable for differential pressure transmitters, balancing high and low-pressure sides.
Practical Applications of Three-Valve Manifolds
These manifolds allow precise pressure balancing, which is critical for accurate differential pressure readings. The equalizing valve simplifies maintenance by ensuring safety during pressure transmitter servicing. They are widely adopted in industries like oil and gas, where accurate pressure monitoring is essential.
Five-Valve Manifold: Features and Use Cases
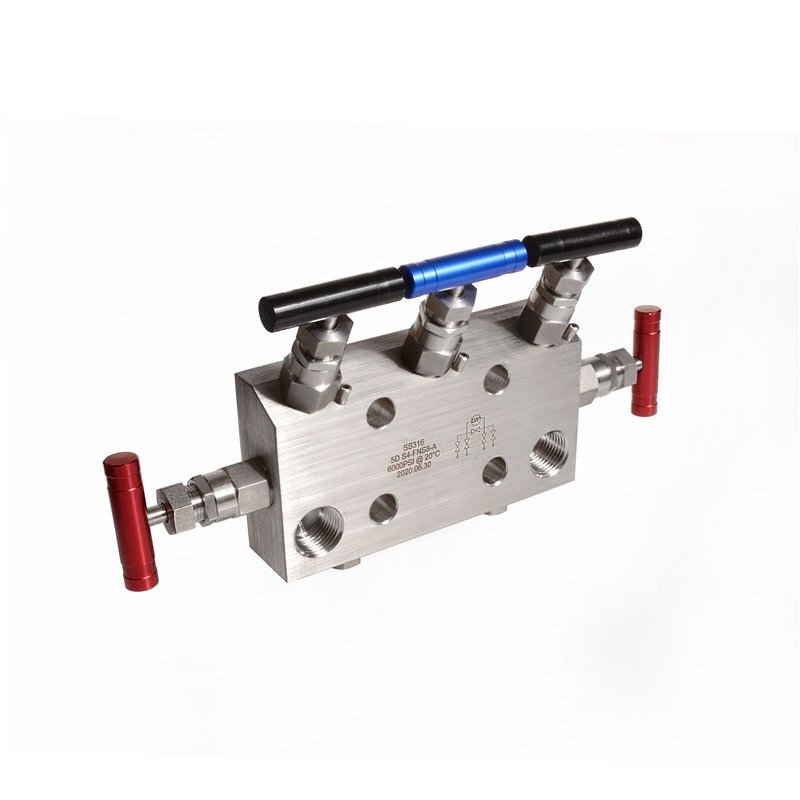

Five-valve manifolds feature two isolation valves, one equalizing valve, and two vent valves. This configuration offers the highest level of versatility.
Five-valve manifolds are used in advanced operations such as transmitter calibration, fluid venting, and system maintenance.
Why Choose a Five-Valve Manifold?
Five-valve manifolds provide comprehensive control for complex systems. With dedicated venting and isolation capabilities, they minimize risks during system intervention. They are ideal for high-precision industries, such as power generation and chemical processing, where both reliability and flexibility are paramount.
Comparison Table: Types of Manifold Valves
| Type | Number of Valves | Key Functions | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Two-Valve | 1 Isolation, 1 Vent | Isolation and venting | Pressure gauge calibration and isolation |
| Three-Valve | 2 Isolation, 1 Equalizing | Isolation, balancing high and low sides | Differential pressure transmitters |
| Five-Valve | 2 Isolation, 1 Equalizing, 2 Vent | Isolation, venting, and calibration | Complex systems in oil, gas, and power |
Materials and Design Configurations
Manifold valves are crafted from materials like 316 stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy 400, each suited for specific environments.
Material selection depends on factors like system pressure, fluid compatibility, and environmental conditions. Direct-mount, remote-mount, and modular designs further enhance their adaptability.
Comparing Materials and Designs
316 stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for harsh environments. Alloy 400 excels in marine and chemical applications due to its resilience to aggressive fluids. Modular designs allow for easy expansion, while remote-mount systems enable flexibility in compact setups.
Operating Principles of Manifold Valves
Using manifold valves requires adherence to specific operating procedures for safety and efficiency.
Each valve type operates with a defined sequence of steps to manage pressure isolation, venting, or balancing. Following these steps ensures optimal functionality.
Step-by-Step Guide to Operation
- Two-Valve Manifold: Close the isolation valve, open the vent valve to release pressure, and proceed with calibration.
- Three-Valve Manifold: Equalize pressure using the equalizing valve before servicing transmitters.
- Five-Valve Manifold: Carefully isolate and vent system fluids during complex maintenance tasks.
Clear labeling and regular operator training are key to safe and efficient valve operation.
Applications Across Industries
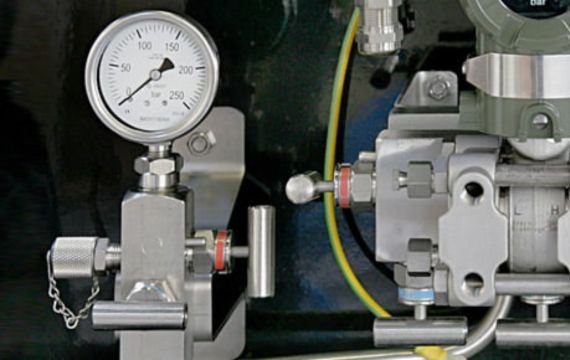
Manifold valves are utilized in sectors like oil and gas, petrochemicals, power generation, and water treatment.
Their ability to manage fluid control effectively ensures process safety, system reliability, and improved performance across industries.
Real-World Applications
- Oil and Gas: Used in wellhead control panels to ensure accurate pressure monitoring and safe operations.
- Chemical Processing: Critical for managing fluid flows in highly reactive environments.
- Water Treatment: Provide precise control in filtration and purification processes.
By ensuring proper pressure management and reducing risks, manifold valves enhance operational efficiency and safety across diverse applications.
Selection and Maintenance Guide

Choosing the right manifold valve involves evaluating pressure ratings, temperature range, and fluid compatibility.
Proper selection ensures system reliability, while regular maintenance extends valve lifespan and minimizes failures.
Maintenance Best Practices
- Inspect valves regularly for signs of wear or corrosion.
- Clean vent ports and moving parts to prevent blockages.
- Test valve functionality periodically to identify potential issues early.
Maintaining detailed logs of inspections and repairs can help streamline future maintenance efforts.
Emerging Technologies and Trends
Innovations like IoT-enabled monitoring systems and advanced materials are transforming manifold valve design.
Automation and real-time monitoring improve efficiency and reduce manual intervention, paving the way for smarter fluid control systems.
Upcoming Trends
IoT integration enables remote monitoring and diagnostics, reducing downtime. Advanced alloys enhance durability in extreme environments. Modular designs are becoming the standard for customizable, scalable systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the most common material used for manifold valves?
316 stainless steel is the most common material due to its excellent corrosion resistance and durability in harsh environments.
2. How often should manifold valves be maintained?
Manifold valves should be inspected every six months for signs of wear and tested annually to ensure they function properly.
3. Can a single manifold valve be used for multiple applications?
Yes, depending on the design and configuration, a manifold valve can handle multiple functions like isolation, venting, and balancing.
4. What industries benefit most from manifold valves?
Industries like oil and gas, petrochemicals, power generation, and water treatment use manifold valves for efficient fluid control and system reliability.
5. How does IoT integration improve manifold valve performance?
IoT-enabled systems allow real-time monitoring, remote diagnostics, and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Manifold valves are indispensable for efficient and safe fluid control in industrial systems. Selecting the right valve type, coupled with proper maintenance, ensures long-lasting performance and reliability.







